कोशी प्रधेश ५ औ तह सब इन्जिनियर पदमा लोकसेवाले सोधेका प्रश्नहरू


Transition curves are designed to gradually change the alignment from a straight road to a circular curve, reducing the risk of overturning by introducing centrifugal force progressively. This prevents sudden jerks, enhances passenger comfort, and provides a smooth introduction of superelevation and extra widening, which are critical for vehicle stability on curves
In plane table surveying, the intersection method is used to plot inaccessible points. This involves setting up the plane table at two or more stations with known positions and drawing rays toward the target point. The location of the inaccessible point is determined by the intersection of these rays on the map
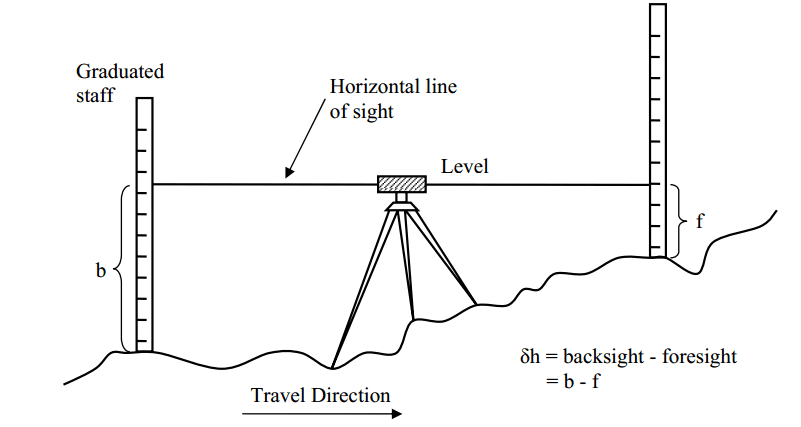
Fly leveling is a method of leveling used in surveying to determine approximate elevations over long distances, especially when the benchmark is far from the work site. In this method, a temporary benchmark is established at the work station based on the original benchmark. It involves rapid measurements using foresight (FS) and backsight (BS) readings, focusing on moderate accuracy rather than precision. Fly leveling is commonly employed for preliminary or rough leveling tasks where high precision is not required


Bitumen is primarily obtained as a byproduct of the distillation of crude oil. It is composed of heavy hydrocarbons and is extracted during the refining process when lighter components like gasoline and diesel are removed. Bitumen can also occur naturally in deposits such as oil sands or tar pits
Tri-calcium silicate (C3S) is the primary compound in cement responsible for early strength development and contributes significantly to the overall quality of cement. It reacts quickly with water, producing calcium hydroxide and heat, which accelerates the hydration process and enhances the cement's compressive strength.
Distemper paints are typically water-based, and water serves as the primary thinner to adjust the paint's consistency for application. This approach is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly. While other solvents like naphtha, turpentine, or olive oil are used in certain types of paints, they are not commonly associated with distemper paints

Slate and marble are both metamorphic rocks, which means they have undergone transformation from their original forms due to high pressure and temperature conditions.
Slate: Formed from shale or claystone, slate is a fine-grained metamorphic rock that splits easily into thin layers.
Marble: Originating from limestone, marble is a dense, crystallized metamorphic rock known for its use in sculptures and buildings.

The frog of a brick is typically made on its top face. This indentation serves multiple purposes, including reducing the weight of the brick, providing a key for mortar to improve bonding during masonry work, and sometimes displaying the manufacturer's name
When a concentrated load is applied to a beam, the shear force at that point experiences a sudden change (discontinuity). Since the slope of the bending moment (BM) diagram at any section equals the shear force at that section14, this abrupt shift in shear force causes a corresponding sudden change in the slope of the BM diagram at the load's location.
When both ends of a column are fixed, its effective length is reduced to 0.5 times the actual length (L). This is because fixed ends provide maximum restraint, preventing rotation and lateral displacement, which increases the buckling resistance of the column
In most pipe flow systems, the pressure inside the pipe is typically greater than atmospheric pressure to ensure the fluid flows efficiently and overcomes frictional losses, elevation changes, and other resistances. This is especially true in pressurized systems where pumps or gravity maintain a higher internal pressure to drive the flow.
The discharge formula is applicable for small orifices, where the head of the liquid above the orifice is significantly greater (more than five times) than the depth of the orifice. In such cases, the velocity of water across the cross-section is approximately constant, allowing this simplified formula to be used effectively
A breast wall is constructed on the hillside of a roadway to retain earth and prevent it from slipping or sliding onto the road. It is specifically designed to support the natural slope of the hill and stabilize the soil, ensuring safety and maintaining the integrity of the roadway.
Specific gravity of soil solids does not directly affect soil compaction. The primary factors influencing compaction include water content, compaction energy, and soil type, as these determine the soil's workability, density, and response to applied mechanical energy. Specific gravity mainly relates to the mineral composition of the soil and is not a direct factor in the compaction process
The bearing capacity of soil depends on multiple factors, including:
- Size of particles: Larger particles, such as in coarse-grained soils (e.g., gravel), generally provide higher bearing capacity due to better interlocking and reduced compressibility.
- Shape of particles: Angular particles offer better interlocking and shear strength compared to rounded particles, increasing the soil's load-bearing capacity.
- Cohesive properties of particles: Cohesion in fine-grained soils, such as clay, contributes to their shear strength and affects the bearing capacity.
Thus, all these factors collectively influence the soil's ability to support loads without failure

In a rectangular beam subjected to transverse shear forces, the distribution of shear stress across any cross-section follows a parabolic curve. The shear stress is maximum at the neutral axis (the horizontal centerline of the beam's depth) and decreases to zero at the top and bottom surfaces. This parabolic distribution is characteristic of rectangular cross-sections under shear loading.
Over-reinforced sections have the highest percentage of steel reinforcement compared to balanced and under-reinforced sections. In these sections, the steel does not yield before the concrete fails, leading to sudden and brittle failure, which is unsafe and generally avoided in design practices
As per IS 456:2000, the minimum diameter of longitudinal reinforcement bars in a column should not be less than 12 mm. This ensures adequate strength and stability of the column under load conditions
The bearing capacity of soil depends on factors like grain size, soil type, moisture content, compaction, and density. Grain size affects the interlocking and frictional resistance between particles, which directly influences the soil's ability to support loads. Options B (Load intensity), C (Depends on the load), and D (Rate of loading) are not direct factors affecting the inherent bearing capacity of the soil but may influence settlement or behavior under specific conditions.
In construction, hacking refers to the process of roughening a surface, such as a wall or concrete slab, before plastering. This roughening creates a better bond between the plaster and the substrate, ensuring the plaster adheres properly and reduces the likelihood of peeling or blistering.
- Dubbing (A): This involves filling low areas or depressions in a surface to level it out before plastering.
- Blistering (C): This is a defect that occurs when bubbles form under the plaster surface, often due to trapped air or moisture.
- Peeling (D): This refers to the detachment or lifting of the plaster from the underlying surface, usually caused by poor adhesion.
Temporary casing is often referred to as formwork, as it provides a temporary structure to support and shape materials like concrete during construction. It is used to stabilize excavations or boreholes temporarily until the concrete or permanent structure is set and can support itself.
Landfill leachate refers to the liquid that forms when water (from precipitation or other sources) percolates through waste in a landfill. This liquid extracts soluble and suspended solids, as well as harmful substances, from the decomposing waste, making it potentially toxic and environmentally hazardous
Manholes are openings constructed on sewer or drain lines to allow personnel to enter or leave the sewer system for inspection, cleaning, maintenance, and repairs. They are essential for accessing underground utilities and are typically covered with a heavy lid for safety and to prevent debris from entering the system
The most suitable location for canal headworks is in the trough stage (or alluvial stage) of a river. In this stage, the river's cross-section is composed of alluvial sand and silt, with a small bed slope and low velocity. This minimizes seepage losses and provides a stable foundation for the headworks. Additionally, irrigation demand is typically high in this stage, making it ideal for constructing canal headworks.
Other stages like the rocky and delta stages are generally unsuitable due to steep slopes, high velocities, or wide cross-sections, which complicate construction and operation.
The duty of water refers to the area of land (in hectares) that can be irrigated with a continuous supply of 1 cubic meter per second (cumec) of water during the entire base period of the crop. It represents the efficiency of water use in irrigation and is typically expressed in hectare/cumec
Note: Since lowering water level in the river is not the primary intention of a diversion headwork the best option is B. If option A) was raising the water level in the river the correct answer would have been all of the above.
Pothole patching is classified as routine maintenance, as it involves regular and ongoing activities to keep roads functional and safe. Routine maintenance typically includes tasks like repairing small damages (e.g., potholes), cleaning drains, and maintaining road signs, which are performed continuously regardless of traffic volume or road conditions
In semi-grouted macadam pavement, also known as grouted macadam, the term "hoggin" refers to a mixture of materials used to fill the voids within the pavement structure. This mixture typically consists of stone powder, which helps in binding the aggregates together, enhancing the pavement's stability and durability.
Deviation of the alignment of a trace cut is generally permitted in areas involving landslides, as these areas pose significant safety risks and challenges to construction. Adjusting the alignment helps avoid unstable zones and ensures the stability and safety of the infrastructure being constructed.
In road construction, the formation width refers to the total horizontal width of land affected by the construction of the road, extending from the top of the cut slope on one side to the top of the cut slope on the other side. This width encompasses the entire roadway, including the carriageway (the portion of the road used by vehicles) and shoulders, as well as any embankments or cuttings.
Valuation is typically done to determine the market value, which represents the price an asset would fetch in a competitive and open market. This approach ensures that the valuation reflects the current economic conditions and the asset's worth based on demand, supply, and other market factors.
The quantity of shutters for doors and windows is calculated in square meters (m²), as it involves determining the area of the shutter (length × height). This unit is commonly used for woodwork, plastering, painting, and other surface-related measurements
Illustrative sketches are not an essential part of the general specification for public works. General specifications primarily focus on material details, work methodology, and the mode of measurement for payment to ensure clarity and compliance in construction processes. Sketches or drawings are typically included in separate documents like blueprints or detailed design plans, rather than in the general specifications.
Scrap value, also known as salvage value or residual value, refers to the estimated worth of an asset's components or materials when the asset has reached the end of its useful life and is no longer in service. This value represents the amount that can be recovered from selling the asset's parts or materials as scrap
Tender documents typically include components such as the tender form, Bill of Quantities (BOQ), and the amount of earnest money, but they do not specify unit rates directly. Unit rates are usually provided by the bidders during the tendering process as part of their cost estimation and proposal.
A flexible pavement of a runway typically consists of the surface course, base course, and sub-base course. These layers work together to distribute loads, resist deformation, and provide durability. The surface course is the topmost layer made of asphalt, the base course provides structural support, and the sub-base course further distributes loads to the subgrade beneath




